Sustainable management towards drought and fire resilience
Supporting fire- and drought-resilient ecosystems remains a global challenge, especially in arid regions where fresh water is a limited resource. My research identifies sustainable management strategies that benefit ecosystem services under drought. Recently, I have considered the tradeoffs between water use and crop growth using remote sensing data under different management and climate scenarios. As we found in our paper, although intensive irrigation in farmland can create local temperature depressions that benefit human health, it may also result in unsustainable water use long-term. Balancing these needs is crucial for a more sustainable future.
Keep an eye out for our upcoming paper on how sustainable management practices improve agricultural water-use efficiency!
 Cropland, vegetation cover and evapotranspiration over Davis, California
Cropland, vegetation cover and evapotranspiration over Davis, California
Near-surface remote sensing for drought detection and carbon dynamics
Pairing satellite-based sensors with instruments deployed from the ground – on drones, towers, airplanes, or from your hand – helps us understand the global signals we see from space. I use field-based experiments to consider how systems respond under varying management interventions and water limitiation. I am also interested in developing low-cost sensors for applications in industry and citizen science.
Along with a team of other scientists and students, I deployed an ultra-hyperpsectral imager at field sites in California. The imager takes ‘pictures’ of photosynthesis across a landscape, capturing differences in carbon fixation rates between individual plants and even leaves. This signal, solar-induced fluorescence (SIF), is a phenomenon of plants ‘glowing’ as they perform photosynthesis and capture carbon from the atmosphere. Rates of photosynthesis can change instantaneously depending on environmental conditions and are sensitive to water stress, making SIF a useful drought indicator.
We’re working with the hyperpsectral imager to answer questions about drought, soil warming, and plant disease on carbon fixation rates. This work will help us understand terrestrial ecosystem functionality and predict carbon cycling under climate change. Check out our new paper on our SIF fieldwork published in Geophysical Research Letters.
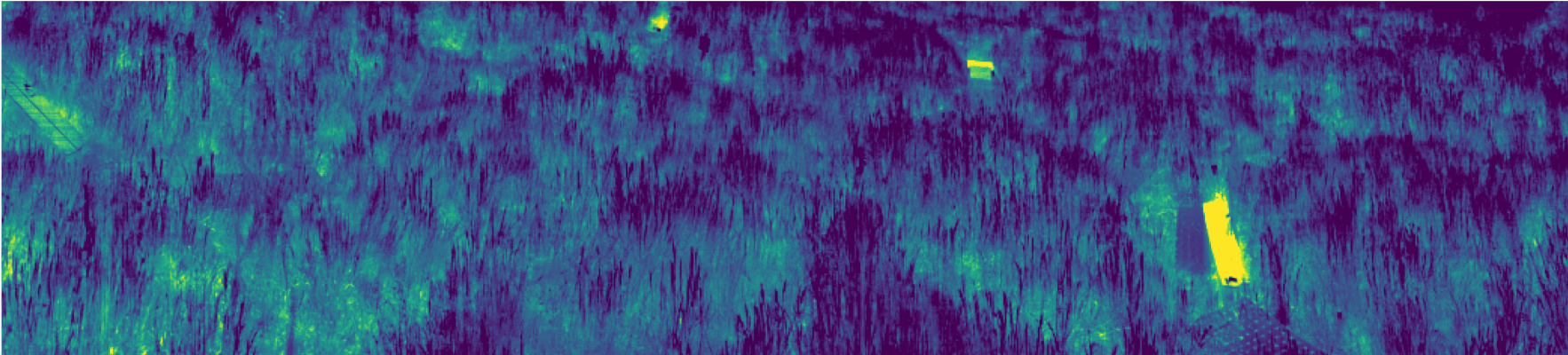 SIF at a grassland in Point Reyes, CA
SIF at a grassland in Point Reyes, CA
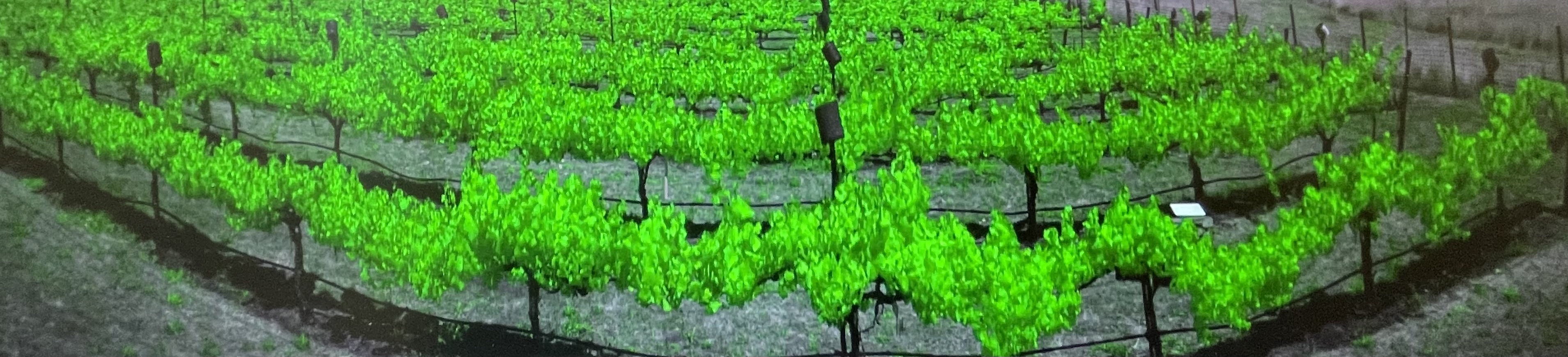 SIF at an experimental vineyard in Hopland, CA
SIF at an experimental vineyard in Hopland, CA
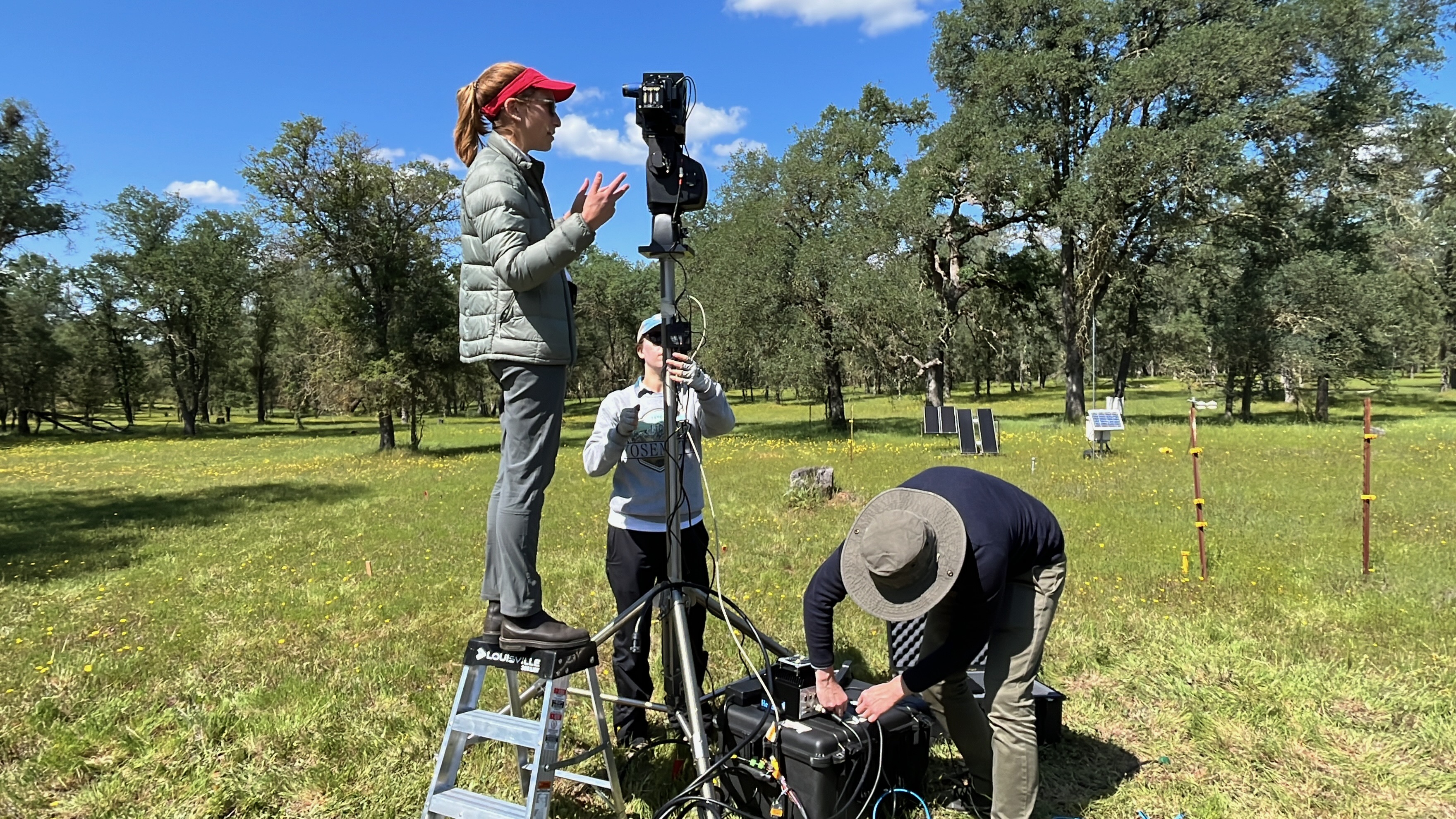 The team at an AmeriFlux site deploying a hyperspectral imager
The team at an AmeriFlux site deploying a hyperspectral imager
Advancing mechanistic understanding through ecohydrology
Ecosystems rely on water to grow and thrive. When plants take up carbon through tiny pores on their leaves, called stomata, they also release water into the atmosphere. This inherent tradeoff can determine rates of carbon sequestration at the ecosystem and regional scale. I use remote sensing and eddy covariance flux tower data to untangle the effects of water scarcity on ecosystems, with the goal of predicting carbon cycling and ecosystem function under future climate change.
Recently, we considered the role of groundwater in modulating carbon uptake. Plants in arid and semi-arid systems often rely on groundwater throughout the year and during droughts. In our recent paper, we found that groundwater drought can diminish carbon fixation and sequestration rates by almost 20%. Since groundwater is a critical freshwater resource for both people and ecosystems, understanding these complex and often over-looked interactions is important for regional water budgets, along with climate mitigation and adaptation goals.
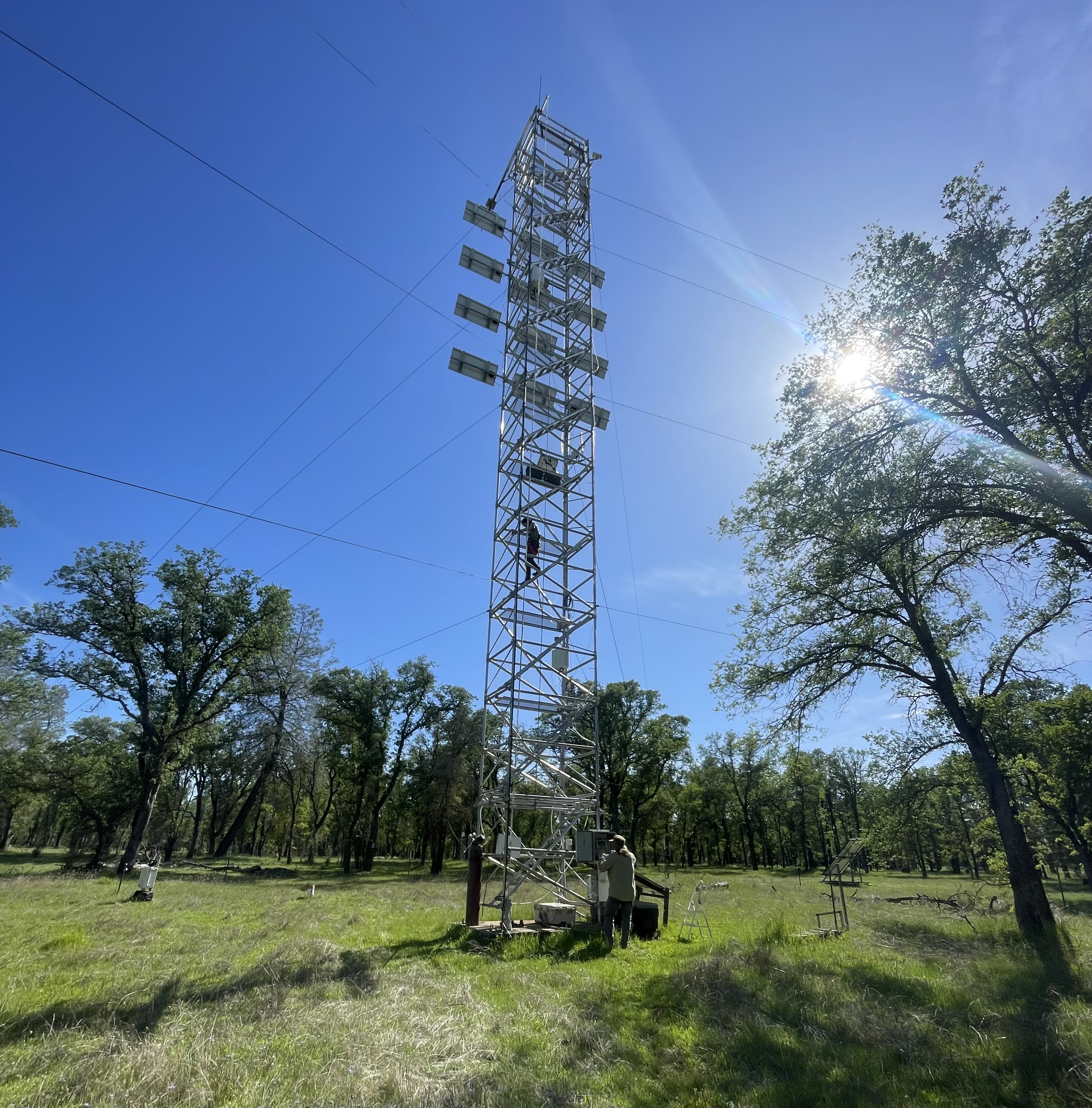 A groundwater-dependent ecosystem in the Sierra Nevada foothills
A groundwater-dependent ecosystem in the Sierra Nevada foothills
People have developed many ways of studying the environment, and not all of these frameworks have historically been respected by western science. Yet these stewardship practices and observational techniques can provide fresh insights on environmental issues. As a journalist and oral historian, I value stakeholder perspectives throughout the research process. In Vanuatu, where I undertook paleoclimate and oral history research, I learned how migration, global economies, and kinship networks affect communities’ strategies to remain safe and connected under a changing climate. This experience motivates me to work with stakeholders to improve our research’s applicability and identify policy implications.
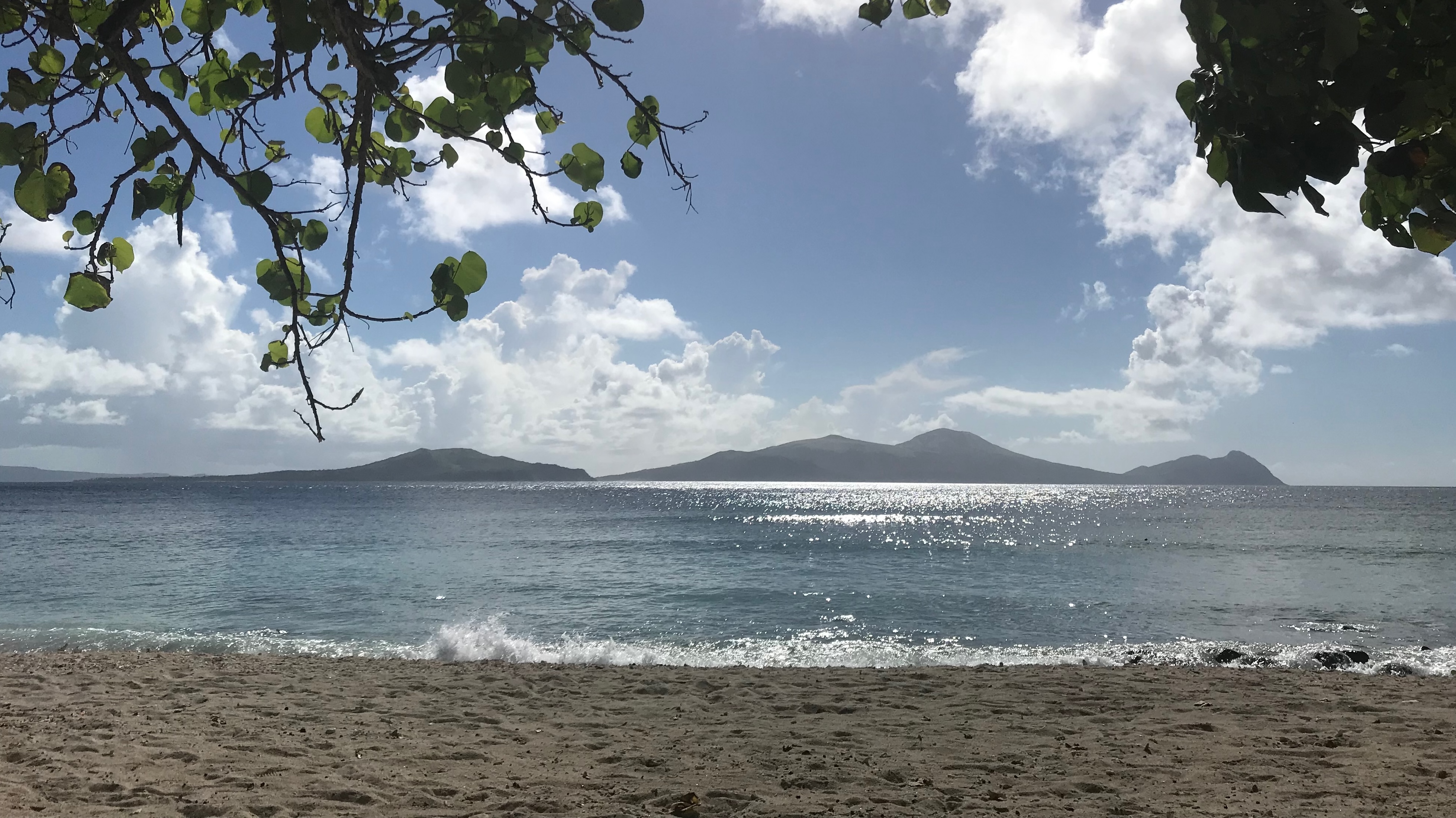 In Vanuatu, intensifying cyclones and drought threaten coastal communities
In Vanuatu, intensifying cyclones and drought threaten coastal communities